Wi-FiマイコンESP32-DevKitC-32EとAndroidとの
BLE通信
温度センサBMP280ブレイクアウトボード使用
2023.9.29 Coskx Lab
1 はじめに
温度センサBMP280を載せたWi-FiマイコンESP32-DevKitC-32EからAndroidスマホに向けてBLE(Bluetooth Low Energy)を使って温度情報を送ります。
Wi-FiマイコンとAndroidスマホ間の通信は無線LAN環境の下ではHTTPでの通信ができますが,無線LAN環境がない場合では,Bluetooth通信が便利です。
ESP32-DevKitC-32EはBLEを使って通信します。(Bluetooth Classicではありません。)
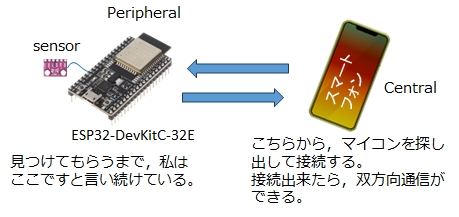
BLEコネクション通信では,Central(or Master or Observer)とPeripheral(or Slave or Broadcaster)の間で通信が行われます。
ここでは,AndroidをCentral,ESP32-DevKitC-32EをPeripheralとして使うことにします。
ここで使用するAndroidスマホのアプリ"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"は起動の度に,通信相手を探して接続するようになっているため,ペアリング(ボンディング)を必要としていません。(ペアリングしておいてもOKです。)
2 使用環境
- Windows 10 64-bit
- ArduinoIDE 2.2.1
- ESP32-DevKitC-32E (ESP32-WROOM-32E)
- BMP280 (HW-611 E/P 280)
- Android Pixel4a + "Serial Bluetooth Terminal"
3 準備
3.1 ArduinoIDE
(1)Arduino IDEのメニューバーから[ファイルFile] -> [環境設定(Preferences)]
Additional board manager URLsに
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/gh-pages/package_esp32_index.json
を設定してOK
(2)ツール[Tools] > ボード[Board] > Boards Manager
検索boxに「ESP」を入力すると複数のボード候補が出てくるので
esp32 by Espressif Systems
をinstall
(3)ツール[Tools] > ボード[Board]でESP32を探すとESP32 Dev Moduleが見つかるので,これを選ぶ。
3.2 ESP32-DevKitC-32E
ESP32-DevKitC-32Eの説明書を読んでプログラムの転送方法を確認します。
(USBケーブルでつないで書き込むだけでした。)
4 ESP32-DevKitC-32Eと温度センサBMP280の配線
温度センサBMP280は温度をデジタル値に変換しているので,そのデータをESP32-DevKitC-32Eが読み出します。
ESP32-DevKitC-32Eと温度センサBMP280はI2C接続ですので,電源線,GND線の他はSCLとSDAの2本のみで通信できます。
CSBをVCCにつなぐとBMP280はI2C接続になります。(データシートによれば確実にVCCにつなぐべきとなっています)
SDO(シルク印刷は間違えていてSDDとなっている)をVCCにつなぐとBMP280のI2Cアドレスは77になります。GNDにつなぐとBMP280のI2Cアドレスは76になります。Groveライブラリのデフォルトは77なのでVCCにつないでいます。
なおBMP280ではSDA,SCLをpullupせずに動作しています。
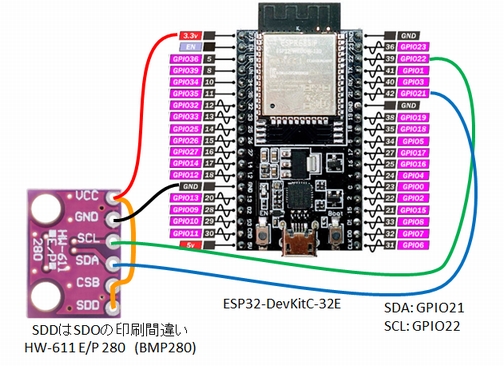
ESP32-DevKitC-32Eと温度センサBMP280の配線
ESP32-DevKitC-32Eと温度センサBMP280
5 ESP32-DevKitC-32Eのスケッチコード(サーバプログラム)
クライアント(Androidスマホ)からのリクエストで,サーバであるESP32-DevKitC-32Eは,温度センサBMP280の値を取得し,クライアントに返します。
送受信ではBLE UART通信の手順に従います。
ESP32-DevKitC-32Eは文字列"start"を受け取ったら1秒間隔で温度などのデータを送信し,文字列"stop"を受け取ったら送信をやめるようにします。
UART通信ですので,プログラム中の受信のパートと送信のパートが分かれば,そこにやりたいことを書けばよいことになります。
受信時はclass MyCallbacks: public BLECharacteristicCallbacksのonWrite()が呼び出され,std::string rxValueに受信文字列が保存されます。ここが受信のパートになります。
受信パートでは受信文字列が"start","stop"であった時には,作業フラグisrequestedをそれぞれtrue,falseに設定します。
loop()内でdeviceConnected およびisrequestedがtrueで,一定時間が経過したら,温度などを測定して,送信すべきデータ文字列("温度","気圧","標高")を作って,送信します。ここが送信パートになります。
なお,
#define DEVICENAME "UART Service"
は自分の名前です。Androidスマホなどから見つけてもらう名前です。
次のコードは,IDEの既存スケッチ例"BLE_uart.ino"を元に作ったものです。
ライブラリ"Grove_-_Barometer_Sensor_BMP280"を予めIDEに追加しておいてください。
#include <BLEServer.h>
#include <BLEUtils.h>
#include <BLE2902.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include "Seeed_BMP280.h"
#define DEVICENAME "UART Service"
// See the following for generating UUIDs:
// https://www.uuidgenerator.net/
#define SERVICE_UUID "6E400001-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E" // UART service UUID
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_RX "6E400002-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E"
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_TX "6E400003-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E"
BLEServer *pServer = NULL;
BLECharacteristic * pTxCharacteristic;
bool deviceConnected = false;
bool oldDeviceConnected = false;
uint8_t txValue = 0;
boolean isrequested = false;
BMP280 bmp280;
int interval = 1000; //millisec
int currenttime = 0; //millisec
int previoustime = 0; //millisec
class MyServerCallbacks: public BLEServerCallbacks {
void onConnect(BLEServer* pServer) {
deviceConnected = true;
Serial.println("** device connected");
};
void onDisconnect(BLEServer* pServer) {
deviceConnected = false;
Serial.println("** device disconnected");
}
};
class MyCallbacks: public BLECharacteristicCallbacks {
void onWrite(BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic) {
std::string rxValue = pCharacteristic->getValue();
if (rxValue.length() > 0) {
Serial.println("*********");
Serial.print("Received Value: ");
for (int i = 0; i < rxValue.length(); i++)
if (rxValue[i] != '\r' && rxValue[i] != '\n')
Serial.print(rxValue[i]);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("*********");
//Reply as is
pTxCharacteristic->setValue(rxValue);
pTxCharacteristic->notify();
delay(10);
if (rxValue.find("start") != -1) { //"start" has found
pTxCharacteristic->setValue("tempreture[degC], pressure[hPa], altitude[m]\r\n");
pTxCharacteristic->notify();
delay(10);
isrequested = true;
previoustime = millis(); //elapsed time(ms)
previoustime -= interval;
} else if (rxValue.find("stop") != -1) { //"stop" has found
isrequested = false;
}
}
}
};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Create the BLE Device
BLEDevice::init(DEVICENAME); //BLE Device Name scaned and found by clients
// Create the BLE Server
pServer = BLEDevice::createServer();
pServer->setCallbacks(new MyServerCallbacks());
// Create the BLE Service
BLEService *pService = pServer->createService(SERVICE_UUID);
// Create a BLE Characteristic
pTxCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_TX,
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_NOTIFY
);
pTxCharacteristic->addDescriptor(new BLE2902());
BLECharacteristic * pRxCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_RX,
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE
);
pRxCharacteristic->setCallbacks(new MyCallbacks());
// Start the service
pService->start();
// Start advertising
pServer->getAdvertising()->start();
Serial.println("Waiting a client connection to notify...");
//start BMP280
if(!bmp280.init()){
Serial.println("Device error!");
}
}
void loop() {
if (deviceConnected) {
if (isrequested) {
currenttime = millis(); //elapsed time(ms)
if (interval <= currenttime - previoustime) {
previoustime += interval;
float tempreture = bmp280.getTemperature();
float pressure = bmp280.getPressure();
float altitude = bmp280.calcAltitude(pressure);
char string0[256];
sprintf(string0, "%.1f, %.0f, %.2f\r\n", tempreture, pressure/100.f, altitude);
pTxCharacteristic->setValue(string0);
pTxCharacteristic->notify();
delay(10);
}
}
}
// disconnecting
if (!deviceConnected && oldDeviceConnected) {
delay(500); // give the bluetooth stack the chance to get things ready
pServer->startAdvertising(); // restart advertising
Serial.println("start advertising");
oldDeviceConnected = deviceConnected;
}
// connecting
if (deviceConnected && !oldDeviceConnected) {
// do stuff here on connecting
oldDeviceConnected = deviceConnected;
}
delay(2);//allow the cpu to switch to other tasks
}
6 Androidスマホアプリ"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"の準備
Android playから,"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"をダウンロードしてインストールします。
"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"のアイコン
最初の起動で,メニュー等の探検をします。
〇左上三本線メニューでは
settings→terminal→Show timestampをONにしておくとよいでしょう。
settings→terminal→Buffer sizeは表示内容を保存する作業メモリのサイズです。できるだけ大きくとるのが良いと思います。(200kBでは100文字のデータ約2000行分です。場合によっては無制限もあり)
settings→ReceiveはCR+NLが標準ですが,後で受信行での改行が変だったら,適当に変えてください。
settings→Send→Local echoはONが標準です。自分が送信した文字列も表示されます。
settings→Misc.→Save....は表示内容(LOG)保存先フォルダの設定です。
〇右上3点メニューには
Data→Saveがあって,表示内容を保存の時使います。
7 ESP32-DevKitC-32Eと"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"の通信
先にESP32-DevKitC-32Eに電源を与え,立ち上げておきます。

"BMP280が接続されたESP32-DevKitC-32E
その後,"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"で
左上三本線メニューでDevices→BluetoothLE→SCAN で付近のBLEデバイスを見つけて表示してくれます。
ここでは,ESP32-DevKitC-32Eのプログラムの
#define DEVICENAME "UART Service"
でつけた名前"UART Service"が見つかるのでこれをタップします。
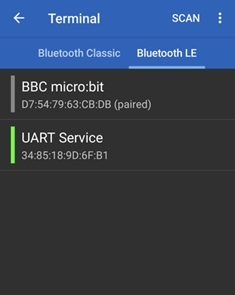
Serial Bluetooth Terminalデバイス選択画面
"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"から"start"を送信すると,1秒ごとにデータが送信されてきます。
受信した3つの数値は温度[℃],気圧[hPa],標高[m]を表しています。
"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"から"stop"を送信すると,データ送信が止まります。
画面上の受信データは,右上3点メニューからData→Saveで保存することができます。
"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"から"start"や"stop"を送信するときは,画面下部のテキストボックスに入力して送信ボタンをタップするか,予めマクロボタンに"start"や"stop"の文字列を登録(マクロボタンのタップ&ホールドで登録出来る)しておいて,それらのボタンをタップます。
次の通信画面では,予めマクロボタンに"start"や"stop"の文字列が登録されています。
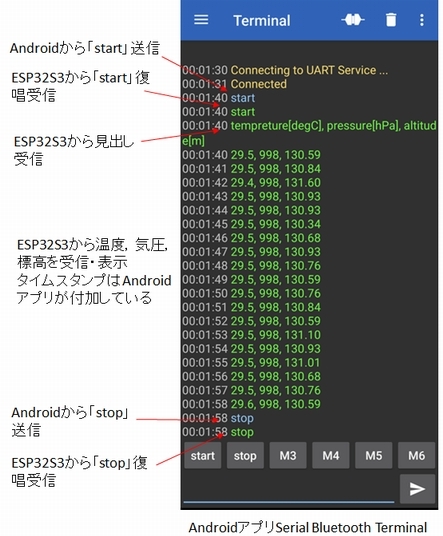
Serial Bluetooth Terminal通信画面
8 通信距離
AndroidスマホをCentralとして,ESP32-DevKitC-32Eとの通信距離を測定しました。
見通しの良い直線で50mまで通信可能でした。
それ以上の距離では,通信が途絶えてしまいました。
9 まとめ
Wi-FiマイコンESP32-DevKitC-32EとAndroidスマホでBLEuart通信し,Androidスマホからの指令によって温度などのデータをESP32-DevKitC-32Eが送って来るようにしました。
ESP32-DevKitC-32E側のプログラムで,受信文字列が見られる部分と,送信したい文字列を送信する部分を示しました。
この記事ではAndroidスマホのアプリ"Serial Bluetooth Terminal"を使いましたが,iPhoneにも同様なアプリがあるので,それが使えると思います。
"BLE serial nRF (free)" がお薦めのようです。
WindowsPCでは同様なアプリは見つかっていません。(BLE対応のデバイスドライバが見つかれば通常のターミナルアプリが使えると思います。)